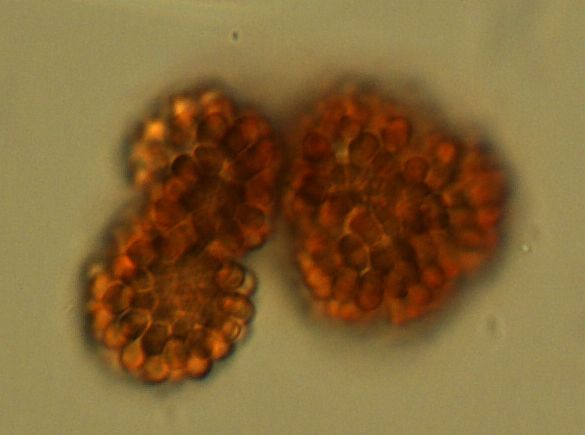
Species details
- Gomphosphaeria naegeliana: Unger, Lemmermann (1907)
- Coelosphaerium naegelianum: Unger (1854)
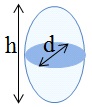
- Cell Length: from 5 to 7 µm
- Cell Width: from 2.5 to 3.5 µm
- Diameter of colony: up to 180 µm
Europe: Spain (Alvarez-Cobelas & Gallardo 1988), Sweden (Skuja 1948). North America: Arkansas (Smith 2010), Minnesota (Hill 1972). South-west Asia: Iran (Afsharzadeh et al. 2003). Asia: China (Hu & Wei 2006). Australia and New Zealand: New South Wales (Day et al. 1995), Victoria (Day et al. 1995).
as Gomphosphaeria naegeliana (Unger) Lemmermann
Europe: Romania (Caraus 2002).
as Woronichinia naegeliana (Unger) Elenkin
Europe: Baltic Sea (Hällfors 2004), Britain (Whitton et al. 2003), Czech Republic (Rajaniemi-Wacklin et al. 2006), Germany (Täuscher 2011, Täuscher 2014), Lithuania (Vitenaite 2001), Luxembourg (Willame et al 2006), Romania (Caraus 2012). North America: Arkansas (Smith 2010). South America: Brazil (Werner 2010). Asia: Korea (Park 2012). South-east Asia: Singapore (Pham et al. 2011).
Possibly toxic.
Resistence Stages:Possibly toxic.
Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae. Oceanographic Methodology series, UNESCO Publishing, 2nd revised edition, Hallegraeff G.M., Anderson D.M., Cembella A.D., 2003,
Checklist of Baltic Sea Phytoplankton Species. Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings No. 95, Helsinki Commission Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission, Hällfors G., 2004,
Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa / Freshwater Flora of Central Europe. 19/1. Cyanoprokaryota. 1. Teil/Part 1: Chroococcales., Spektrum Akademischer Verlag., Komarek J., Anagnostidis K., 2008, 548
Biovolumes and size-classes of phytoplankton in the Baltic Sea, HELCOM Balt.Sea Environ. Proc. No. 106, Olenina I., Hajdu S., Edler L., Andersson A., Wasmund N., Busch S., Göbel J., Gromisz S., Huseby S., Huttunen M., Jaanus A., Kokkonen P., Ledaine I. and Niemkiewicz E., 2006, 1-144
_635192515180960000.jpg)
_635192515241660000.jpg)
_635375677638290000.jpg)
 1.jpg)