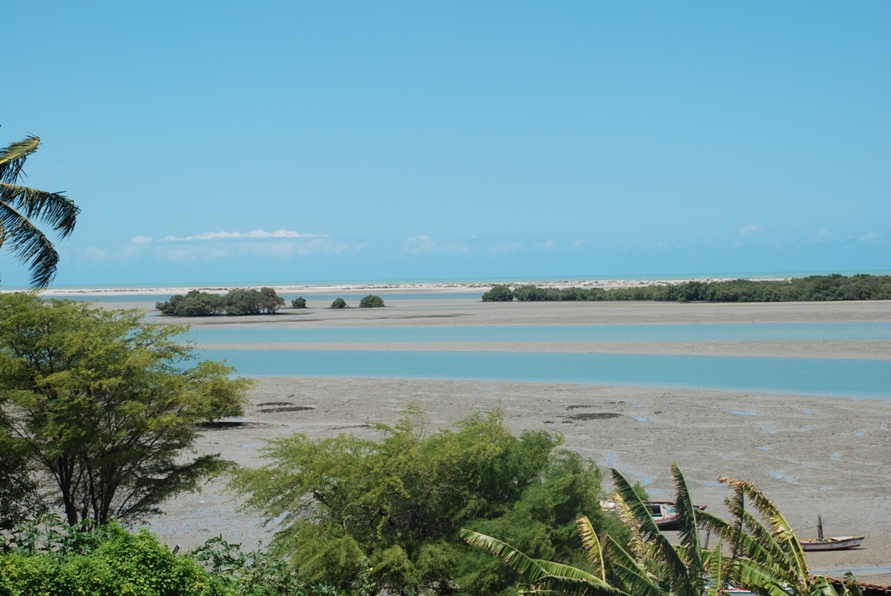
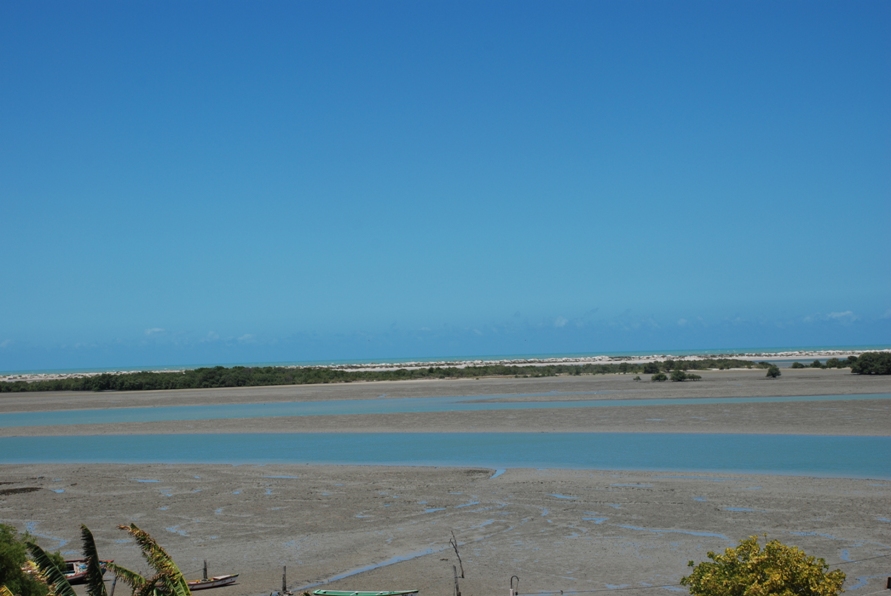
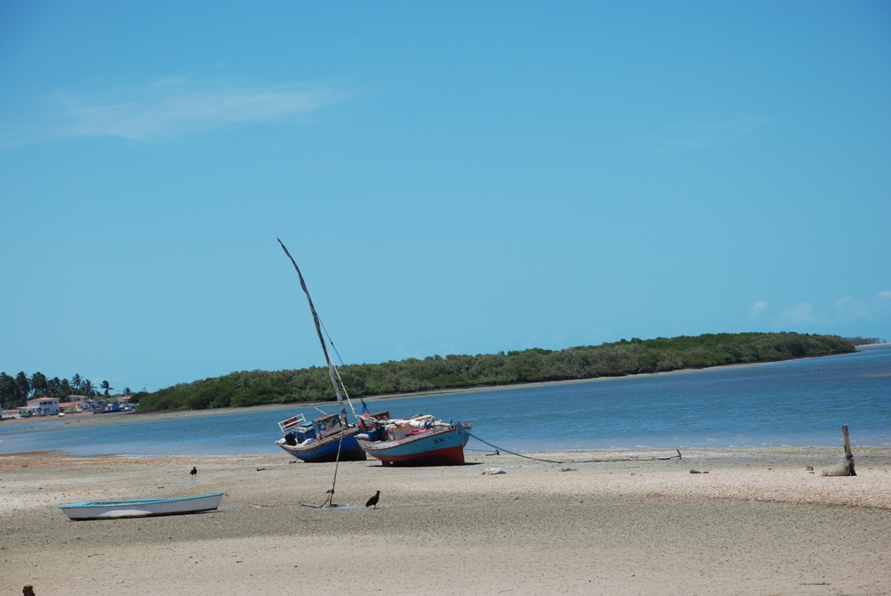
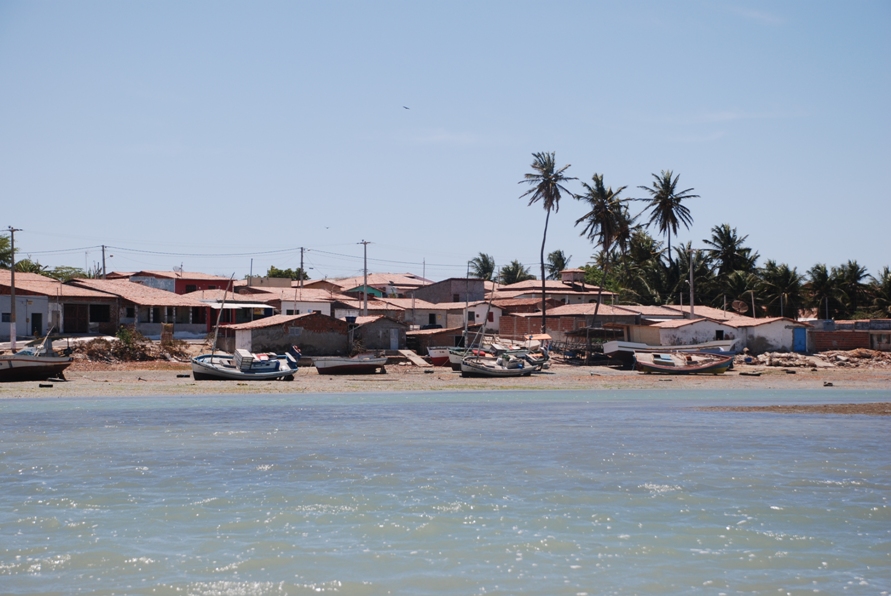
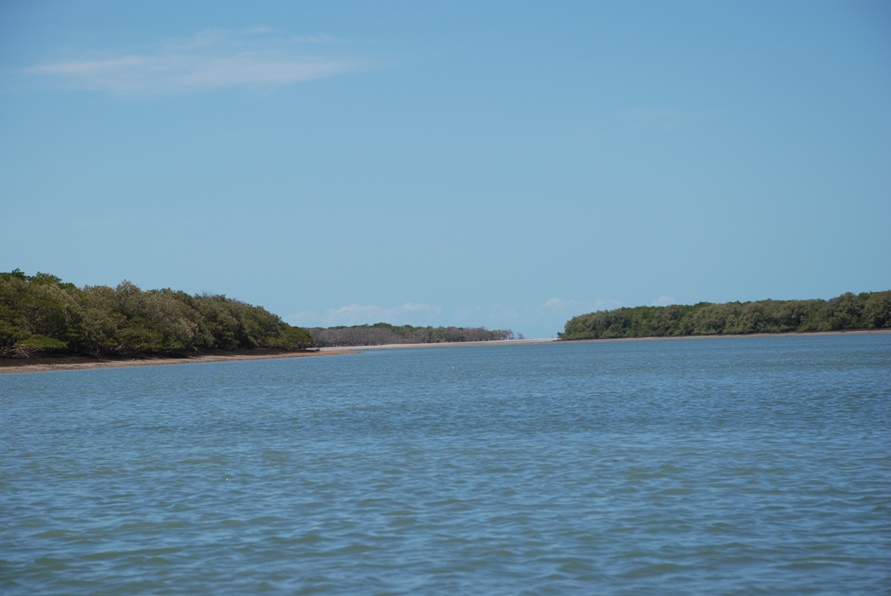
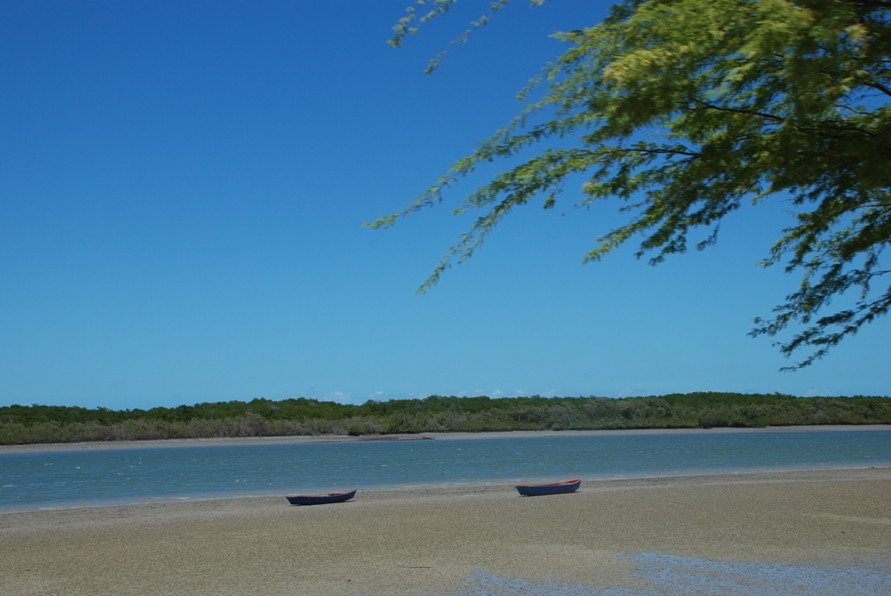
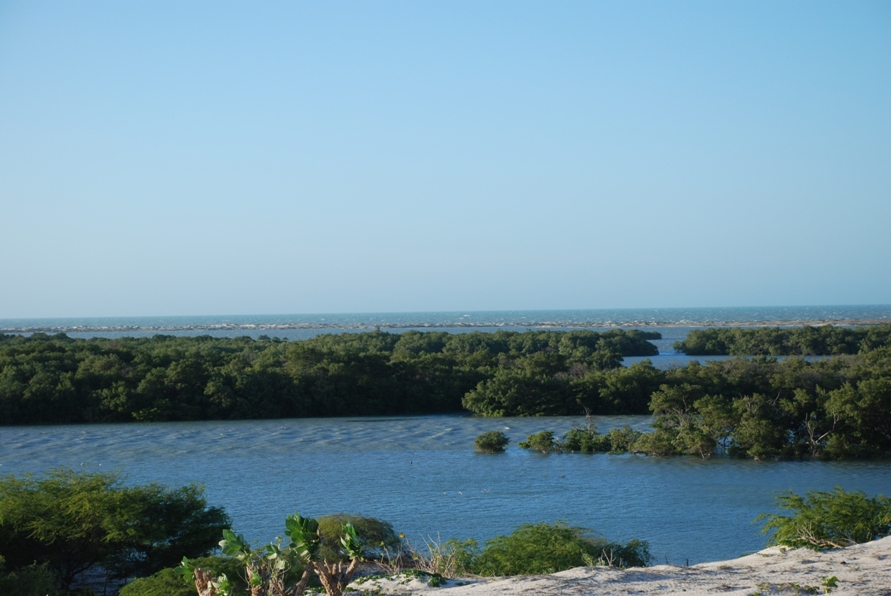
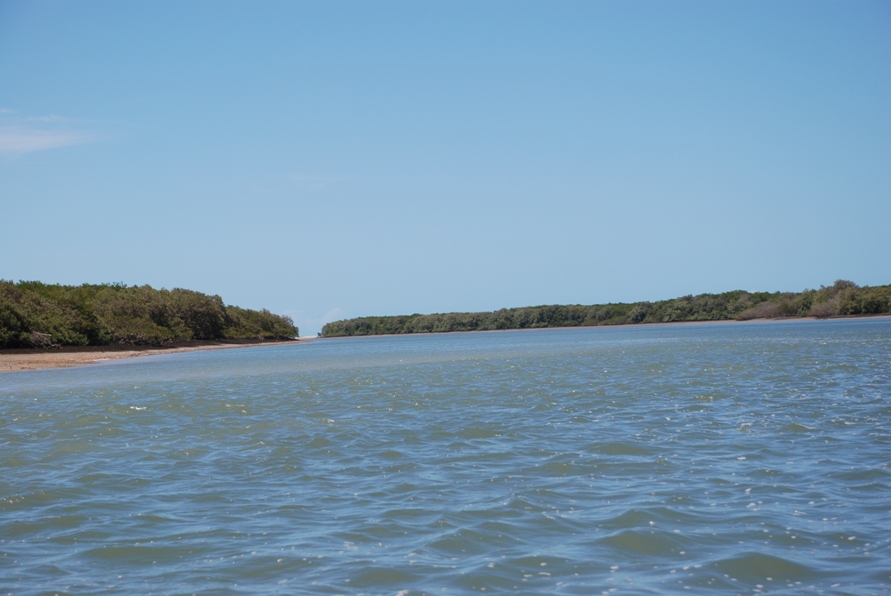
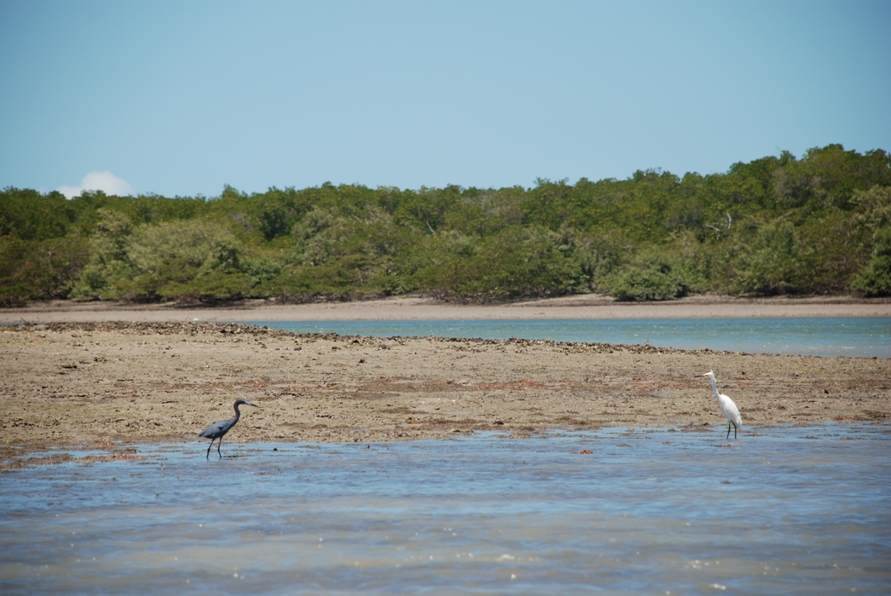
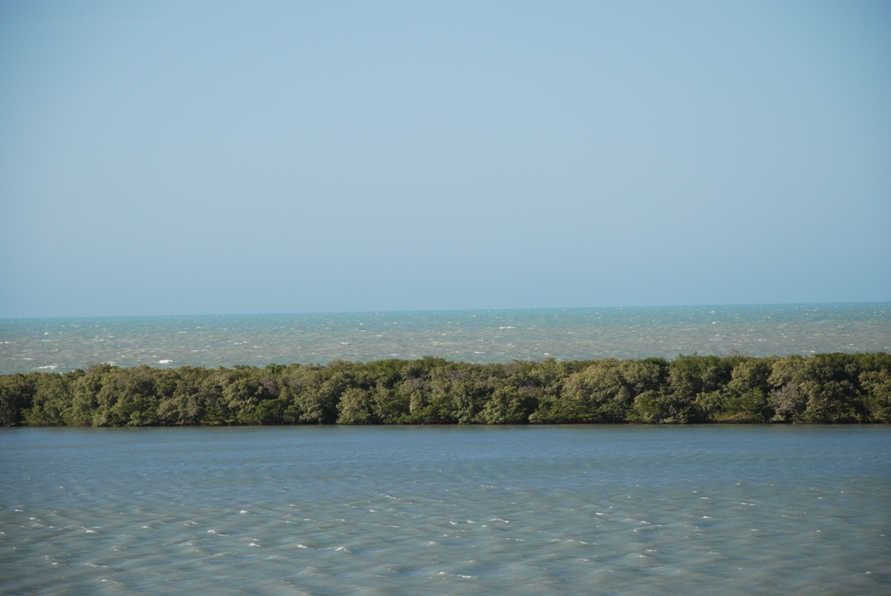
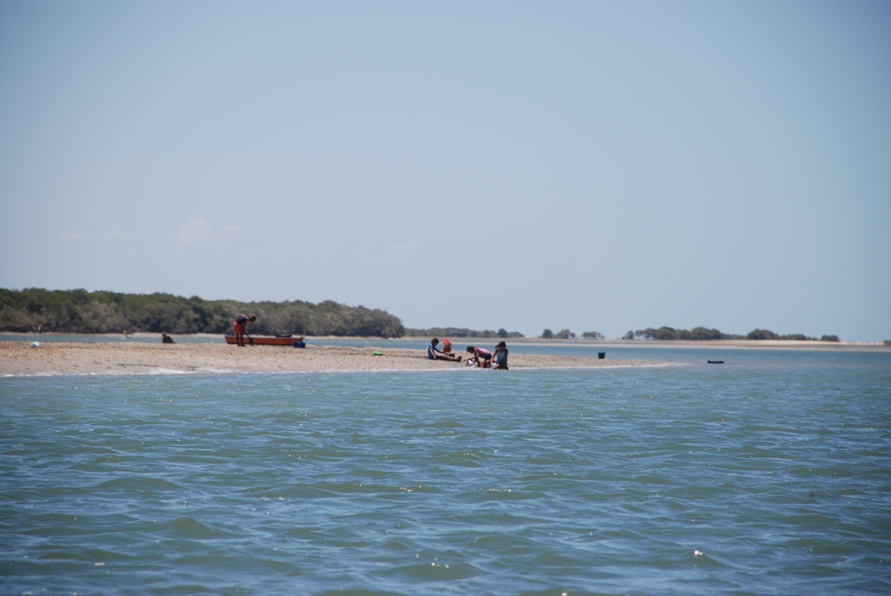
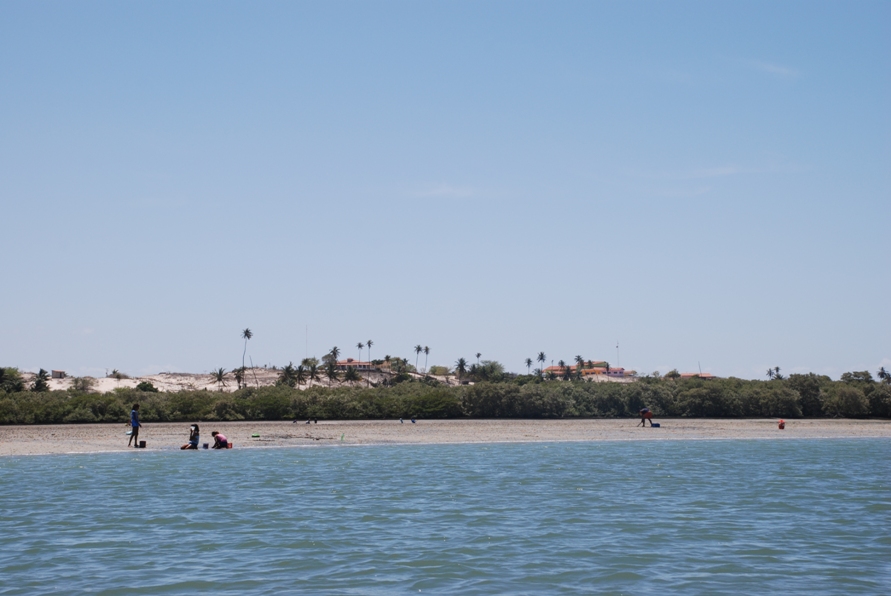
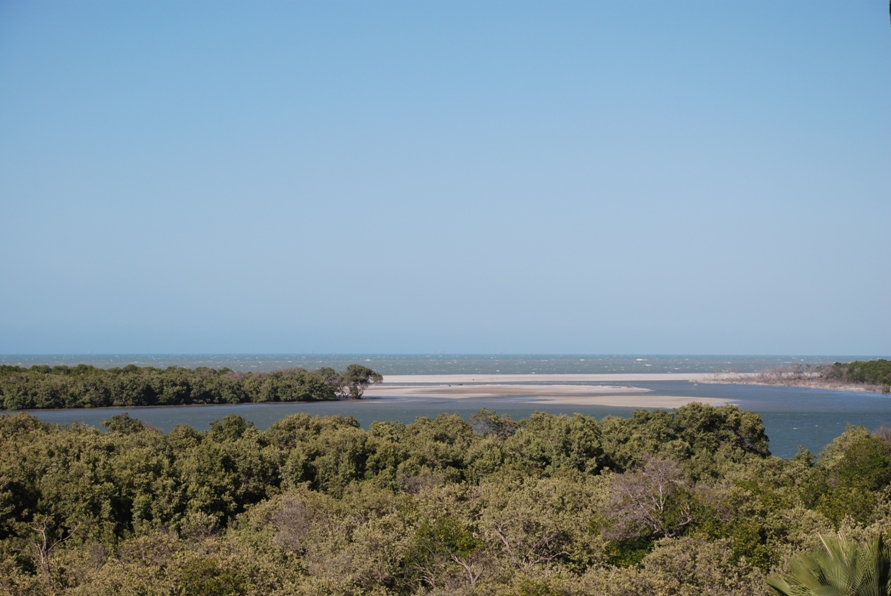
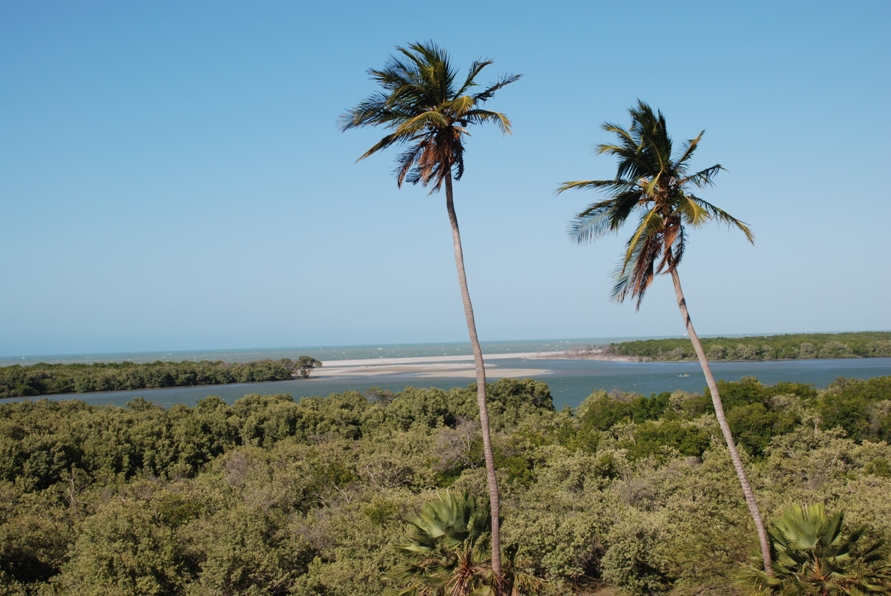
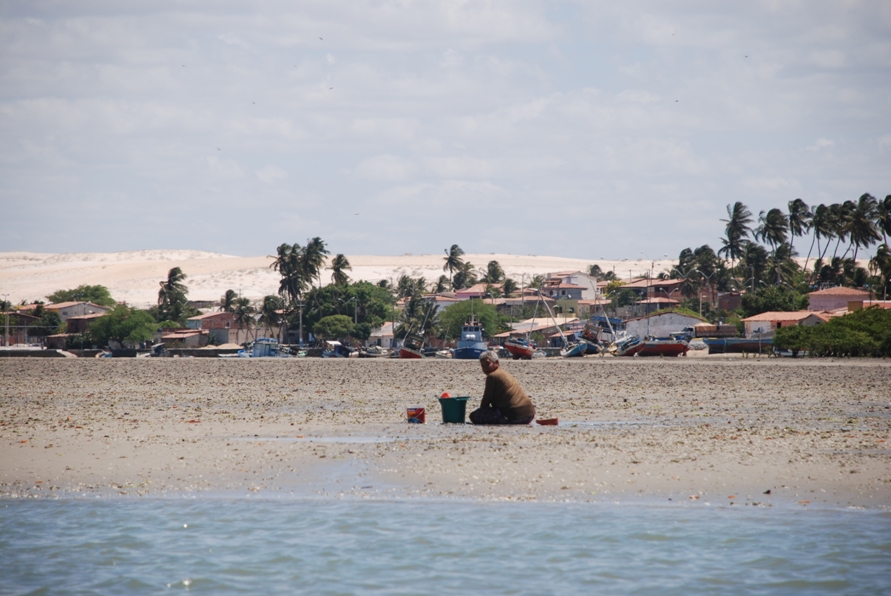
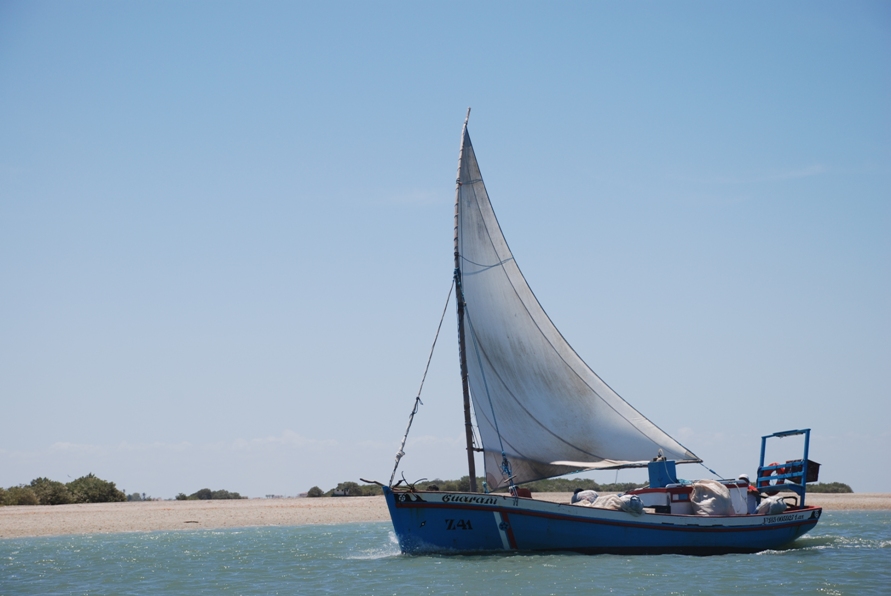
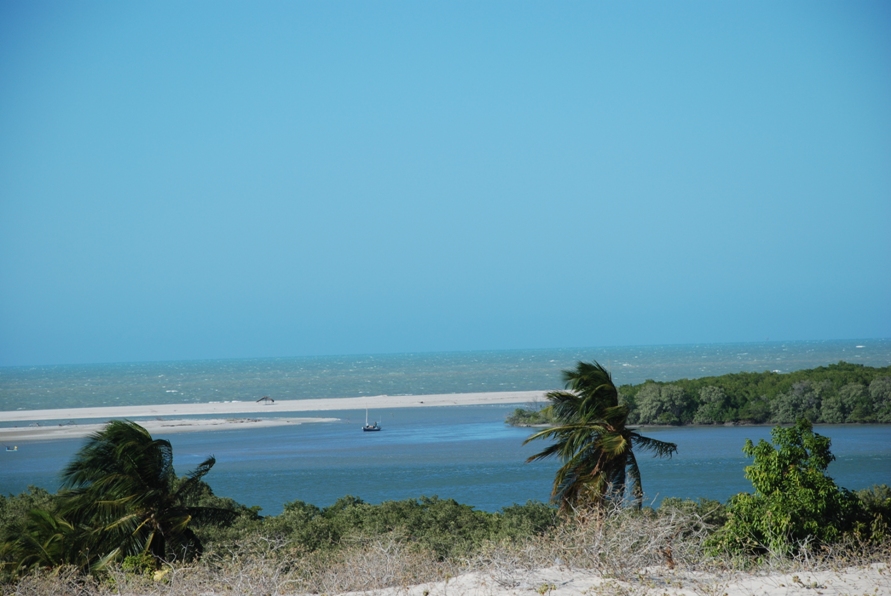
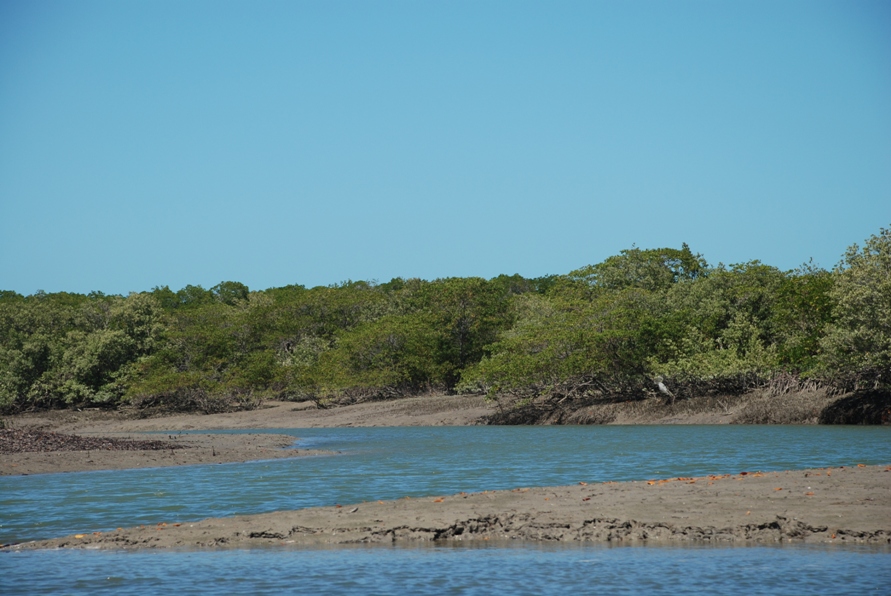
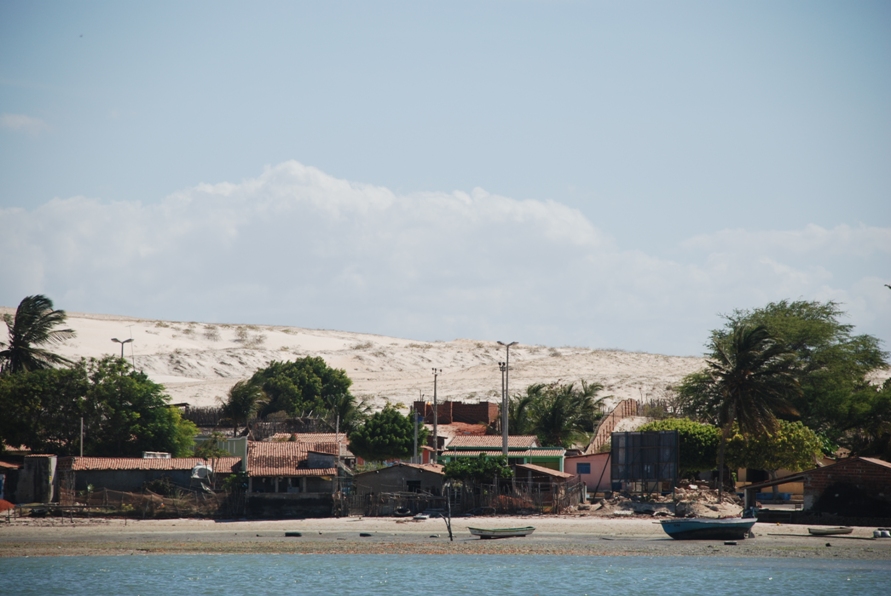
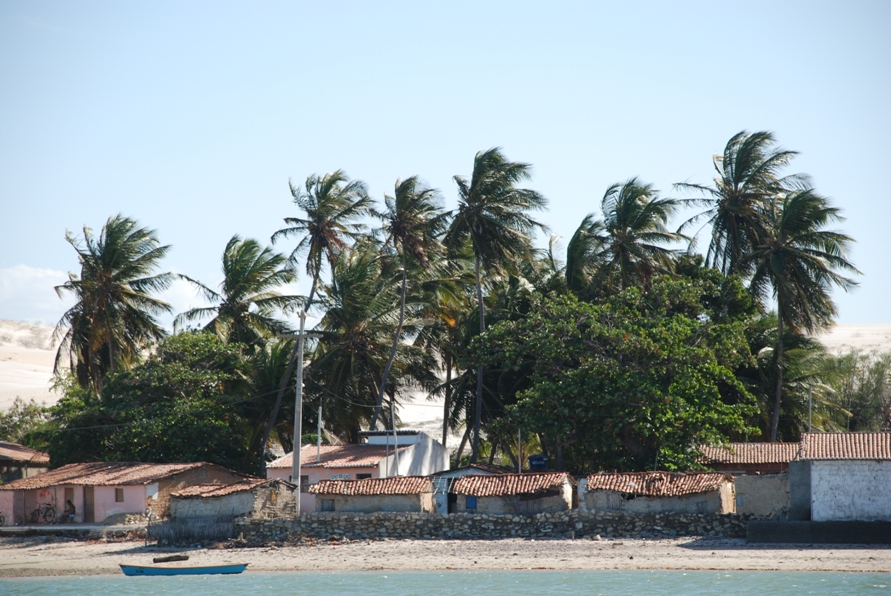
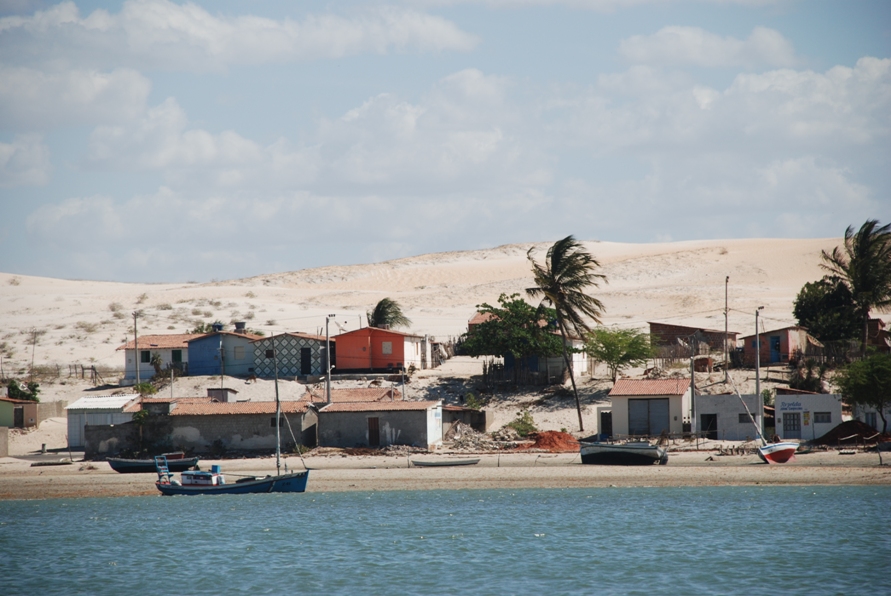
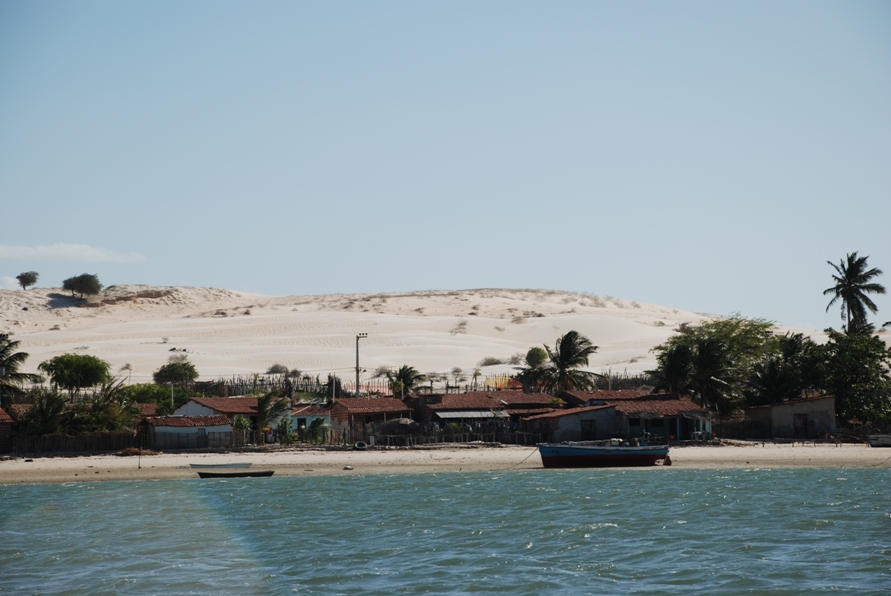
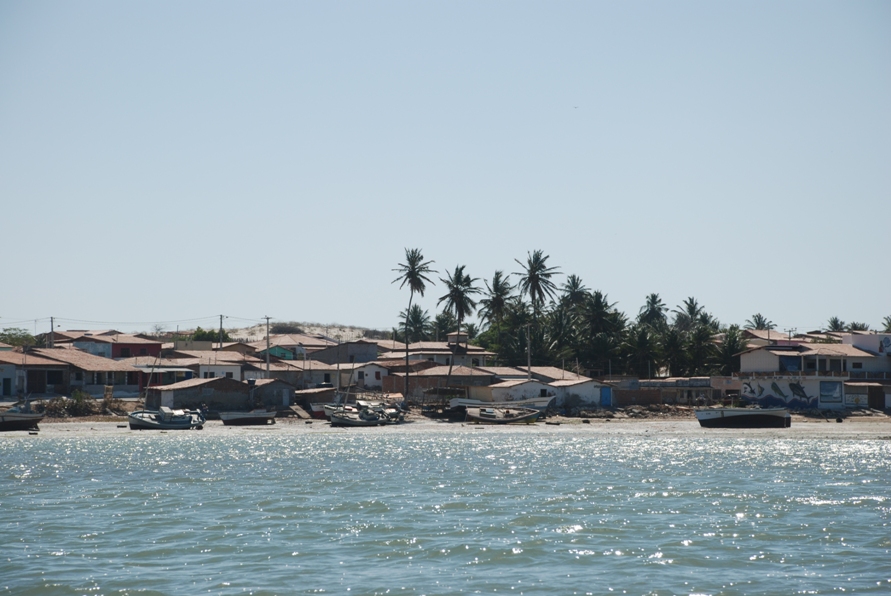
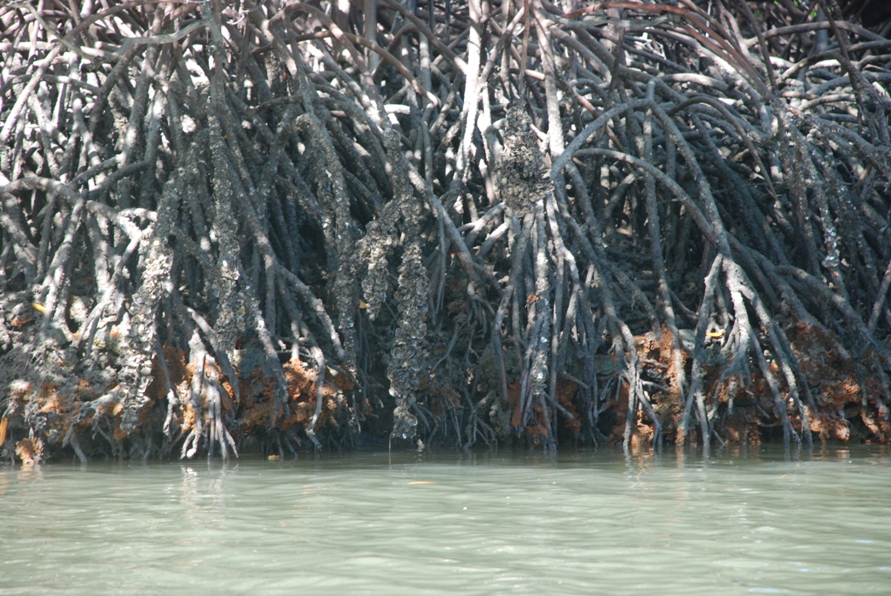
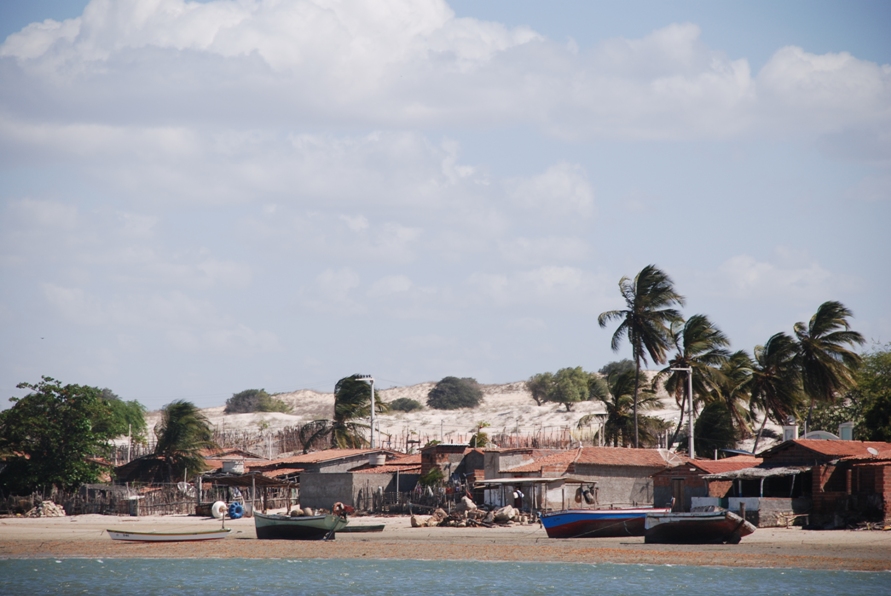
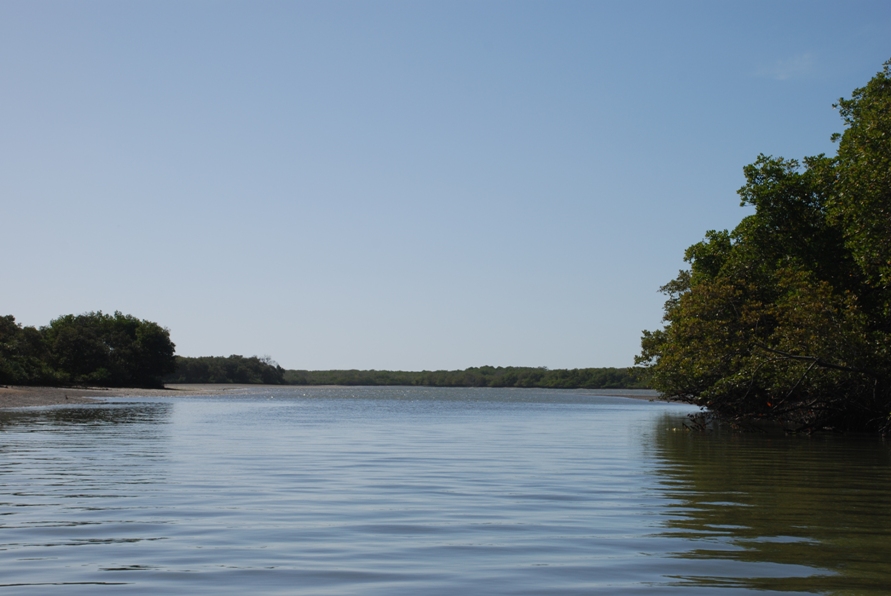
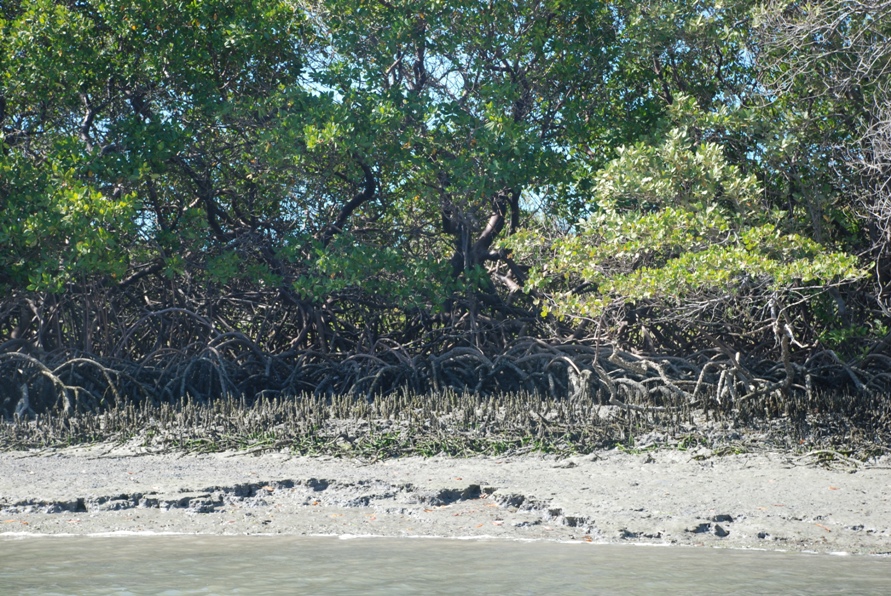
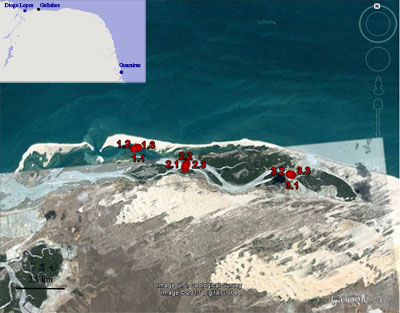
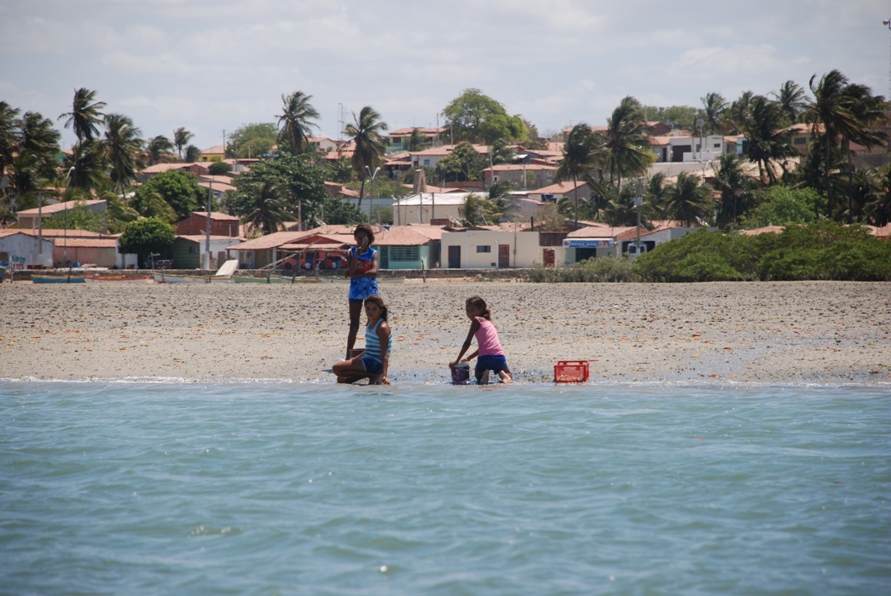Galinhos Lagoon - Brazil
Physical features | |
Physiographic type | Estuarine lagoon (Pisa Sal river) |
Area | – |
Maximum lenght | 6.9 km |
Bathymetr | 6.7 m (high tide) 4.49 m (low tide) |
Wave exposur | Wave height (0.2 – 1.2 m) |
Tidal stream | Weak |
Tidal rang | 0.78 m (high tide) |
Salinity | 38‰ |
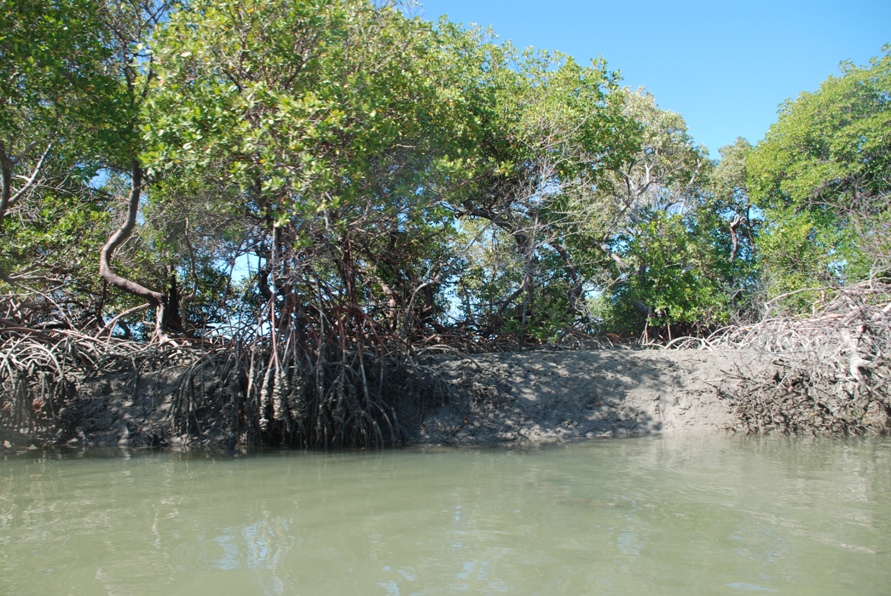
The coastal region of the state of Rio Grande do Norte is long 410 km (11.888 km²). In this area there are many tidal channels, forming hypersaline environments. These environments are composed by the rivers Porto do Campim, Cumurupim, Galinhos, Pisa Sal, Pratagil and Tomás (cities of Galinhos and Guamaré). The estuary of the river Pisa Sal (Galinhos) is the most important, with 6.9km long. The freshwater input occurs by the rain drainage and by the groundwater upwellings. The river mouth flows into the Atlantic Ocean, along with other rivers. The dominant climate in this area is dry with summer rain and scarece rainfall, from march to april.
The average annual rainfall is 600 mm because the Intertropical Convergence Zone, defined by the convergence of the winds from north and south hemispheres.
This region is characterized by a high incidence of light energy, thermal regime uniform, high temperatures and mild variations throughout the year, because of the low latitude, local altitude and strong oceanic influence. The air temperature has an annual average of 26.8ºC.
The daily relative humidity is around 70%, being lower in the months from June to November, coinciding with the season of low rainfall. In this area, the winds blow predominantly from the SE (between the months May to August) E (September to April) and NE (April to September),and the average annual wind speed is 5.7 ms-1. The lowest velocities occur from March to April, while the highest occur between September and October.